QuantiChrom™ Hemoglobin Assay Kit
Application
- For quantitative determination of hemoglobin and evaluation of drug effects on hemoglobin metabolism.
Key Features
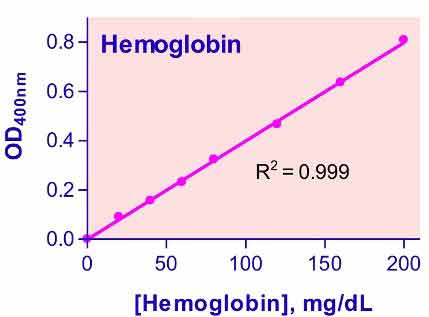
- Sensitive and accurate. Linear detection range 0.9 – 200 mg /dL hemoglobin in 96-well plate assay.
- Simple and high-throughput. The “mix-and-read” procedure involves addition of a single working reagent and reading the optical density. Can be readily automated as a high-throughput assay in 96-well plates for thousands of samples per day.
- Safety. Reagents do not contain any toxic components, e.g. hexacyanoferrate(III) and potassium cyanide used in Drabkin’s reagent.
- Versatility. Assays can be executed in 96-well plate or cuvet.
Method
- OD400nm
Samples
- Blood, serum, plasma, urine etc
Species
- All
Procedure
- 5 min
Size
- 250 tests
Detection Limit
- 0.9 mg/dL
Shelf Life
- 12 months
More Details
HEMOGLOBIN (Hb) is made of four globin chains each carrying a heme group. It is carried by red blood cells and transports oxygen from the lungs to the peripheral tissues to maintain the viability of cells. Quantitation of blood hemoglobin has been a key diagnostic parameter for various diseases such as anemia, polycythemia and dehydration. Simple, direct and automation-ready procedures for measuring hemoglobin concentration are becoming popular in Research and Drug Discovery. BioAssay Systems QuantiChrom™ hemoglobin assay kit is based on an improved Triton/NaOH method, in which the hemoglobin is converted into a uniform colored end product. The intensity of color, measured at 400 nm, is directly proportional to hemoglobin concentration in the sample. The optimized formulation exhibits high sensitivity and is ideal for measuring hemolysis in low hemoglobin samples (e.g. serum and plasma).The procedure mentions that the Standard is to be diluted with water and NO reagent addition. Is the standard already converted cyanohemiglobin? How does this standard reflect OD differences after different incubation times? Wouldn’t you want to create a standard curve for extrapolation of your sample values?
Our assay does not use the cyanohemoglobin method. The “Standard” is not hemoglobin itself as hemoglobin is unstable. We are using a dye at a concentration that gives the same OD reading as the freshly prepared hemoglobin at 100 mg/dL. Therefore when you apply the “Standard”, there is no need to use the reagent.
The changes in OD with incubation time is small if any, but we recommend reading the OD values at 5 min after adding the reagent. The standard curve shown in the protocol was read using a fresh pure hemoglobin preparation and shows that the assay is linear up to 200 mg/dL hemoglobin. Thus there is no need to construct a full standard curve. We recommend using the blank and 100 mg/dL Calibrator to calculate the sample hemoglobin concentration. As long as hemoglobin values are below 200 mg/dL, there is no concern about non-linearity. If it is > 200 mg/dL, we recommend diluting the sample in water and repeat the assay, multiply the value by the dilution factor.
Why can you determine the concentration of hemoglobin in plasma using the kit? I was wondering why the color of plasma (yellow) would not interfere with the measurement of the absorbance at 400 nm. Do you have any data to show that plasma does not interfere with the measurement?
The yellow color of serum is caused mostly by hemoglobin and bilirubin and our assay does not distinguish between the two. However, normal bilirubin levels will add only a relatively minor positive bias which will not elevate the reading above normal hemoglobin levels in serum (< 10 mg/dL). This kit is suitable to test for elevated hemoglobin levels in serum due to hemolysis. If you need to accurately measure the exact hemoglobin concentration in normal serum samples, you probably should take into account the background added by bilirubin. For such applications other assay kits may be more suitable.
Ogasawara, K., et al (2020). Assessment of a downsized potassium adsorption filter designed to transfuse neonates. Transfusion, 60(11), 2494-2499. Assay: Hemoglobin in human filtered blood.
Olatunya, O. S., et al (2019). Red blood cells microparticles are associated with hemolysis markers and may contribute to clinical events among sickle cell disease patients. Annals of Hematology, 98(11), 2507-2521. Assay: Hemoglobin in human plasma.
Liu, C., et al (2020). Salvianolic acid a prevented cerebrovascular endothelial injury caused by acute ischemic stroke through inhibiting the Src signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 42(3), 370-381. Assay: Hemoglobin in rat brain lysate.
Chen, W., et al (2020). MitoQ attenuates brain damage by polarizing microglia towards the M2 phenotype through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome after ICH. Pharmacological Research, 161, 105122. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse brain tissue.
Fornai, M., et al (2020). Protective effects of the combination Bifidobacterium longum plus lactoferrin against NSAID-induced enteropathy. Nutrition, 70, 110583. Assay: Hemoglobin in rat blood.
Imai, T., et al. (2020). Levetiracetam, an Antiepileptic drug has Neuroprotective effects on intracranial hemorrhage injury. Neuroscience, 431, 25-33. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse brain.
Ismael, S., et al. (2020). Tissue plasminogen activator promotes TXNIP-NLRP3 Inflammasome activation after Hyperglycemic stroke in mice. Molecular Neurobiology, 57(6), 2495-2508. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse brain.
Carboni, J., et al (2020). Alterations in the intestinal morphology, gut microbiota, and trace mineral status following intra-amniotic administration (Gallus gallus) of teff (Eragrostis tef) seed extracts. Nutrients, 12(10), 3020. Assay: Hemoglobin in chicken blood.
Colon-Lorenzo, E. et al. (2020). Structure-based screening of plasmodium berghei Glutathione S-transferase identifies CB-27 as a novel Antiplasmodial compound. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse cell media.
Fornai, M., et al (2020). Role of proteinase-activated receptors 1 and 2 in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy. Pharmacological Reports, 72(5), 1347-1357. Assay: Hemoglobin in rat blood.
Pan, X., et al. (2020). YiQiFuMai lyophilized injection ameliorates tpa-induced hemorrhagic transformation by inhibiting cytoskeletal rearrangement associated with ROCK1 and NF-kb signaling pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 262, 113161. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse brain tissue.
Shimatani, K., et al (2021). A novel model of chronic limb ischemia to therapeutically evaluate the angiogenic effects of drug candidates. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 320(3), H1124-H1135. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse matrigel plug.
Yamamoto, J., et al. (2020). Acrylamide-hemoglobin adduct levels in a Japanese population and comparison with Acrylamide exposure assessed by the duplicated method or a food frequency questionnaire. Nutrients, 12(12), 3863. Assay: Hemoglobin in human blood.
Imai, T., et al. (2020). Deferasirox, a trivalent iron chelator, ameliorates neuronal damage in hemorrhagic stroke models. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology, 394(1), 73-84. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse brain lysate.
Chen, H., et al. (2019). Glycyrrhizin prevents hemorrhagic transformation and improves neurological outcome in ischemic stroke with delayed thrombolysis through targeting peroxynitrite-mediated HMGB1 signaling. Translational Stroke Research, 11(5), 967-982 Assay: Hemoglobin in rat brain tissue.
Noh, K., et al (2020). The hidden role of paxillin: Localization to nucleus promotes tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene, 40(2), 384-395. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse matrigel plug.
Lin, H., et al. (2020). Overexpression of FAM46A, a non-canonical Poly(A) polymerase, promotes hemin-induced Hemoglobinization in K562 cells. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 8. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse cells.
Wang, J., et al (2020). Exosomal delivery of AntagomiRs targeting viral and cellular MicroRNAs synergistically inhibits cancer angiogenesis. Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids, 22, 153-165. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse matrigel plug.
Kim, S., et al (2020). Ninjurin 1 dodecamer peptide containing the N-terminal adhesion motif (N-NAM) exerts proangiogenic effects in HUVECs and in the postischemic brain. Scientific Reports, 10(1). Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse matrigel plug.
Bogdanska, J., et al. (2020). Tissue distribution of 14C-labelled perfluorooctanoic acid in adult mice after 1-5 days of dietary exposure to an experimental dose or a lower dose that resulted in blood levels similar to those detected in exposed humans. Chemosphere, 239, 124755. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse tissue.
Naito, M. G., et al (2020). Sequential activation of necroptosis and apoptosis cooperates to mediate vascular and neural pathology in stroke. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(9), 4959-4970. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse blood.
Ritzel, R. M., Al Mamun, A., Crapser, J., Verma, R., Patel, A. R., Knight, B. E. & Liu, F. (2019). CD200-CD200R1 inhibitory signaling prevents spontaneous bacterial infection and promotes resolution of neuroinflammation and recovery after stroke. Journal of neuroinflammation, 16(1), 40. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Wang, A., Singh, S., Yu, B., Bloch, D. B., Zapol, W. M., & Kluger, R. (2019). Cross-linked hemoglobin bis-tetramers from bioorthogonal coupling do not induce vasoconstriction in the circulation. Transfusion, 59(1), 359-370. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice plasma.
Arora, G., Hart, G. T., Manzella-Lapeira, J., Doritchamou, J. Y., Narum, D. L., Thomas, L. M. & Miller, L. H. (2018). NK cells inhibit Plasmodium falciparum growth in red blood cells via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Elife, 7, e36806. Assay: Hemoglobin in human blood.
Fiorentino, N. M., Kimmel, K. A., Suleria, H. A., Joseph, M., Alavi, S., Beyer, R. S., & Lindshield, B. L. (2018). Novel Formulated Fortified Blended Foods Result in Improved Protein Efficiency and Hepatic Iron Concentrations Compared with Corn-Soy Blend Plus in Broiler Chickens. Current developments in nutrition, 2(12), nzy073. Assay: Hemoglobin in chicken blood.
Ismael, S., Zhao, L., Nasoohi, S., & Ishrat, T. (2018). Inhibition of the NLRP3-inflammasome as a potential approach for neuroprotection after stroke. Scientific reports, 8(1), 5971. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice brain tissue.
Li, M., Chen, S., Shi, X., Lyu, C., Zhang, Y., Tan, M. & Shen, J. (2018). Cell permeable HMGB1-binding heptamer peptide ameliorates neurovascular complications associated with thrombolytic therapy in rats with transient ischemic stroke. Journal of neuroinflammation, 15(1), 237. Assay: Hemoglobin in rats blood.
Lyu, X., Wang, J., Guo, X., Wu, G., Jiao, Y., Faleti, O. D. & Yang, X. (2018). EBV-miR-BART1-5P activates AMPK/mTOR/HIF1 pathway via a PTEN independent manner to promote glycolysis and angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS pathogens, 14(12), e1007484. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Rojas-Quintero, J., Wang, X., Tipper, J., Burkett, P. R., Zuniga, J., Ashtekar, A. R. & Jimenez, L. (2018). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 deficiency protects mice from severe influenza A viral infection. JCI insight, 3(24). Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Wang, A. (2018). Acetylated Hemoglobin Bis-Tetramers: From Chemical Designs to Physiological Impacts (Doctoral dissertation). Assay: Hemoglobin in rat blood.
Alhusban, A., Kozak, A., Pillai, B., Ahmed, H., Sayed, M. A., Johnson, M. H. & Fagan, S. C. (2017). Mechanisms of acute neurovascular protection with AT1 blockade after stroke: Effect of prestroke hypertension. PloS one, 12(6), e0178867. Assay: Hemoglobin in rats blood.
Niego, B. E., Broughton, B. R., Ho, H., Sobey, C. G., & Medcalf, R. L. (2017). LDL receptor blockade reduces mortality in a mouse model of ischaemic stroke without improving tissue-type plasminogen activator-induced brain haemorrhage: towards pre-clinical simulation of symptomatic ICH. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS, 14(1), 33. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Solstorm, F. (2017). The effect of water currents on post-smolt Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar (L.). A welfare approach to exposed aquaculture. Assay: Hemoglobin in fish blood.
Xiao, X., Nakatsu, G., Jin, Y., Wong, S., Yu, J., & Lau, J. Y. (2017). Gut microbiota mediates protection against enteropathy induced by indomethacin. Scientific reports, 7, 40317. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice feces.
Fournier, P., Dussault, S., Fusco, A., Rivard, A., & Royal, I. (2016). Tyrosine phosphatase PTPRJ/DEP-1 is an essential promoter of vascular permeability, angiogenesis, and tumor progression. Cancer research, 76(17), 5080-5091. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Kanayasu-Toyoda, T., Tanaka, T., Kikuchi, Y., Uchida, E., Matsuyama, A., & Yamaguchi, T. (2016). Cell-Surface MMP-9 Protein Is a Novel Functional Marker to Identify and Separate Proangiogenic Cells from Early Endothelial Progenitor Cells Derived from CD133+ Cells. Stem Cells, 34(5), 1251-1262. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse blood.
Kuo, Z. K., Lin, M. W., Lu, I. H., Yao, H. J., Wu, H. C., Wang, C. C. & Yen, J. H. (2016). Antiangiogenic and antihepatocellular carcinoma activities of the Juniperus chinensis extract. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 16(1): 277. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Muenster, S., Beloiartsev, A., Yu, B., Du, E., Abidi, S., Dao, M. & Fernandez, B. O. (2016). Exposure of stored packed erythrocytes to nitric oxide prevents transfusion-associated pulmonary hypertension. Anesthesiology: The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, 125(5), 952-963. Assay: Hemoglobin in lamb blood.
Wang, W., Li, M., Wang, Y., Li, Q., Deng, G., Wan, J. & Wang, J. (2016). GSK-3beta inhibitor TWS119 attenuates rtPA-induced hemorrhagic transformation and activates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway after acute ischemic stroke in rats. Molecular Neurobiology 53(10): 7028-7036. Assay: Hemoglobin in rat blood.
Wu, S. Y., Rupaimoole, R., Shen, F., Pradeep, S., Pecot, C. V., Ivan, C. & McGuire, M. H. (2016). A miR-192-EGR1-HOXB9 regulatory network controls the angiogenic switch in cancer. Nature communications, 7, 11169. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
Zhang, Z. X., Jin, W. J., Yang, S., & Ji, C. L. (2016). BRAF kinase inhibitor exerts anti-tumor activity against breast cancer cells via inhibition of FGFR2. American journal of cancer research 6(5): 1040-52. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice blood.
French CJ, et al (2010). Vascular rhexis: loss of integrity of coronary vasculature in mice subjected to myocardial infarction. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235(8):966-73. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice tissue.
Liu D et al (2010). Puma is required for p53-induced depletion of adult stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 12(10):993-8. Assay: Hemoglobin in mouse tissue.
Meyer C, et al (2010). Hemodialysis-induced release of hemoglobin limits nitric oxide bioavailability and impairs vascular function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 55(5):454-9. Assay: Hemoglobin in human plasma.
Singleton PA, et al (2010). Methylnaltrexone potentiates the anti-angiogenic effects of mTOR inhibitors. J Angiogenes Res. 2(1):5. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice tumor tissue.
He Y, et al (2009). Effects of cerebral ischemia on neuronal hemoglobin. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29(3):596-605. Assay: Hemoglobin in rat brain tissue.
Kasiappan R, et al (2009). Loss of p53 and MCT-1 overexpression synergistically promote chromosome instability and tumorigenicity. Mol Cancer Res. 7(4):536-48. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice tumor tissue.
Weis SM, et al (2008). Compensatory role for Pyk2 during angiogenesis in adult mice lacking endothelial cell FAK. J Cell Biol. 181(1):43-50. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice tumor tissue.
Burne-Taney MJ, et al (2006). Decreased capacity of immune cells to cause tissue injury mediates kidney ischemic preconditioning. J Immunol. 176(11):7015-20. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice spleen cell.
Thaker PH, et al (2006). Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 12(8):939-44. Assay: Hemoglobin in mice tumor tissue.
To find more recent publications, please click here.
If you or your labs do not have the equipment or scientists necessary to run this assay, BioAssay Systems can perform the service for you.
– Fast turnaround
– Quality data
– Low cost
Please email or call 1-510-782-9988 x 2 to discuss your projects.
$429.00
For bulk quote or custom reagents, please email or call 1-510-782-9988 x 1.
Orders are shipped the same day if placed by 2pm PST
Shipping: RT
Carrier: Fedex
Delivery: 1-2 days (US), 3-6 days (Intl)
Storage: 4°C upon receipt
Related Products
You may also like…
| Name | SKU | Price | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuantiChrom™ Heme Assay Kit | DIHM-250 |
$439.00 |
|
| QuantiChrom™ BCP Albumin Assay Kit | DIAP-250 |
$409.00 |
|
| QuantiChrom™ BCG Albumin Assay Kit | DIAG-250 |
$409.00 |
|
| QuantiChrom™ Hemoglobin Assay Kit | DIHB-250 |
$429.00 |
Why BioAssay Systems
Quality and User-friendly • Expert Technical Support • Competitive Prices • Expansive Catalogue • Trusted Globally
