Polylactate Assay Service
Polymer Quantification
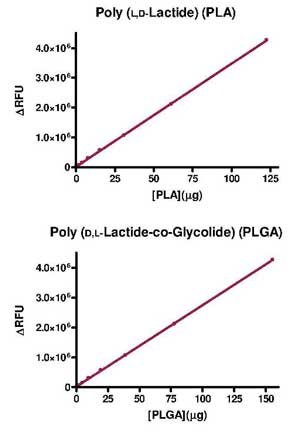
BioAssay Systems has developed a kinetic fluorometric assay to quantify D-lactate containing polymers, such as PLA and PLGA in tissue samples. The assay principle is based on the hydrolysis of D-lactate containing polymers into lactate monomers followed by D-lactate determination using a highly sensitive and specific fluorescence method. Only L-lactate is naturally prevalent in animal tissue (D-lactate is typically present at only nM levels in mammals which is below the detection limit of the current assay); therefore, any D-lactate measured in a sample is solely derived from the polymer present in the sample.
Key Features of the Assay
- Useful to assess remaining polymer coatings on implanted medical devices.
- Two step process: 1) Hydrolysis of polymer present to monomers and 2) Measurement of D-lactate.
- Accuracy and sensitivity of the assay are not affected by polymer MW, which will decrease over time during implantation.
- The method uses D-lactate as a biomarker and since D-lactate is not found endogenously above nM concentrations, the assay is highly specific for PLA.
- There is no requirement to remove the tissue from sample, the PLA on both the device and in the tissue are measured together.
- Depending on the nature of the sample and polymer composition, sensitivities as low as 1 microgram are possible.

Conclusions
This service includes the final preparation of samples for the assay, the hydrolysis of polymer in samples down to monomers and enzymatic measurement of the resultant D-lactate monomers. The polymer weight in the sample is computed from the measured D-lactate concentration in the hydrolysis reaction. The client will be issued a report summarizing the results of the analysis along with an Excel spreadsheet containing all of the collected data, data analysis and results.
Hear What Our Customers Say About Our Services




