EnzyChrom™ Sialic Acid Assay Kit
Application
- For quantitative determination of free and total sialic acid (NANA) and evaluation of drug effects on its metabolism.
Key Features
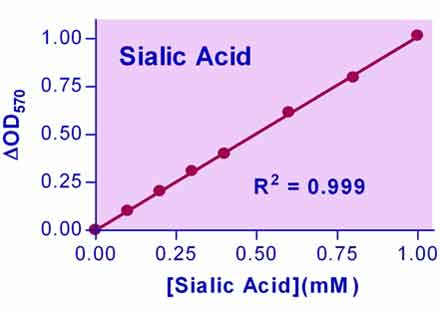
- Sensitive and accurate. Use as little as 10 µL samples. Linear detection range in 96-well plate: 0.02 to 1 mM sialic acid for colorimetric assays and 2 to 100 µM for fluorimetric assays.
- Simple and convenient. Can detect free sialic acid by the addition of a single working reagent and incubation for 60 min at room temperature or total sialic acid by pre-treating samples with a 60 min hydrolysis step.
Method
- OD570nm, or FL530/585nm
Samples
- Biological
Species
- All
Procedure
- 2 hrs
Size
- 100 tests
Detection Limit
- OD, FL: 20, 2 µM
Shelf Life
- 6 months
More Details
- Sialic acid is a general name for nine-carbon acidic sugars with N- or O-substituted derivatives. The most common member of these sugars is N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA). Sialic acid is widely distributed throughout mammalian tissues and fluids including serum. Sialylated oligosaccharides have been shown to exhibit antiviral properties and are also known to influence blood coagulation and cholesterol levels. The Sialic acid level in body fluids is also an important marker for diagnosing cancer. Simple, direct, and automation-ready procedures for measuring sialic acid concentrations find wide applications in research and drug discovery. BioAssay Systems’ sialic acid assay uses a single Working Reagent that combines NANA aldolase, pyruvate oxidase, and hydrogen peroxide determination in one step. The color intensity of the reaction product at 570nm or fluorescence intensity at λex/em = 530/585nm is directly proportional to the sialic acid concentration in the sample
No frequently asked questions for this new product. Please check back later.
For more detailed product information and questions, please feel free to email us. Or for more general information regarding our assays, please refer to Technical Support.
Cadaoas, J., et al. (2021). Galactosialidosis: Preclinical enzyme replacement therapy in a mouse model of the disease, a proof of concept. Molecular Therapy – Methods & Clinical Development. 20: 191-203. Assay: Sialic acid in mouse urine.
Ha, T. K., et al. (2020). Knockout of sialidase and pro-apoptotic genes in Chinese hamster ovary cells enables the production of recombinant human erythropoietin in fed-batch cultures. Metabolic Engineering. 57: 182-192. Assay: Sialic acid in hamster cell line recombinant erythropoietin.
Mosca, R., et al. (2020). Conventional and unconventional therapeutic strategies for sialidosis type I. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 9(3): 695. Assay: Sialic acid in mouse urine.
Odaka, H., et al. (2021). An iPSC-based neural model of sialidosis uncovers glycolytic impairment-causing presynaptic dysfunction and deregulation of Ca2+ dynamics. Neurobiology of Disease. 152: 105279. Assay: Sialic acid in human fibroblast.
Chrostek, L et al (2014). Serum Sialic Acids Levels According to the Severity of Liver Cirrhosis. Journal of clinical laboratory analysis. Assay: Sialic acid in human serum.
Chrostek, L et al (2014). Sialic acid level reflects the disturbances of glycosylation and acute-phase reaction in rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol International. 34(3):393-9. Assay: Sialic acid in human serum.
Ganther, M et al (2014). Partial synthesis of ganglioside and lysoganglioside lipoforms as internal standards for MS quantification. J Lipid Res. 55(12):2692-704. Assay: Sialic acid in bovine brain gangliosides.
Ha, TK, Kim, YG, Lee, GM (2014). Effect of lithium chloride on the production and sialylationof Fc-fusion protein in Chinese hamster ovary cell culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 98(22):9239-48. Assay: Sialic acid in hamster ovary cells.
Bonten, EJ et al (2013). Chaperone-mediated gene therapy with recombinant AAV-PPCA in a new mouse model of type I sialidosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease 1832.10: 1784-1792. Assay: Sialic acid in mouse kidney tissue.
Park, KH et al (2013). Structural and biochemical characterization of the broad substrate specificity of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron commensal sialidase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics1834.8: 1510-1519. Assay: Sialic acid in B. thetaiotaomicron cells.
Sarangarajan, R et al(2011). Methods for treatment of a sarcoma using an epimetabolic shifter (CoEnzyme Q10). US Patent Appl. US 2011/0064747 A1. Assay: Sialic Acid in lipoproteins.
Cylwik B et al (2010). The changes of sialic acid concentration and content in apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the sera of alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol. 45(5):422-6. Assay: Sialic acid in human serum.
Cylwik B, et al (2010). The changes of sialic acid concentration and content in apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the sera of alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol. 45(5):422-6. Assay: Sialic acid in lipoproteins.
To find more recent publications, please click here.
If you or your labs do not have the equipment or scientists necessary to run this assay, BioAssay Systems can perform the service for you.
– Fast turnaround
– Quality data
– Low cost
Please email or call 1-510-782-9988 x 2 to discuss your projects.
$569.00
For bulk quote or custom reagents, please email or call 1-510-782-9988 x 1.
Orders are shipped the same day if placed by 2pm PST
Shipping: On Ice
Carrier: Fedex
Delivery: 1-2 days (US), 3-6 days (Intl)
Storage: -20°C upon receipt
Related Products
You may also like…
| Name | SKU | Price | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuantiChrom™ Sialic Acid Assay Kit | DSLA-100 | $549.00 |
Why BioAssay Systems
Quality and User-friendly • Expert Technical Support • Competitive Prices • Expansive Catalogue • Trusted Globally
