Kinase Inhibitor Screening Service
BioAssay Systems has developed and validated a variety of proprietory methods for follow-up study and HTS screening of kinase inhibitors.
1. IMAP Kinase Assay
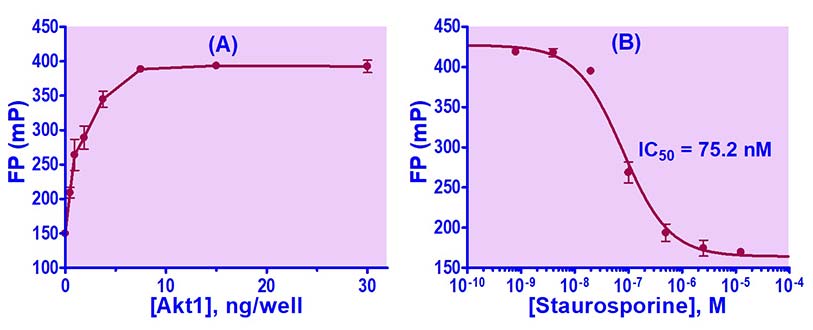
Please contact us by email or call 1-510-782-9988 x 2 to discuss your kinase screening service needs.
2. EKIN Kinase Assay
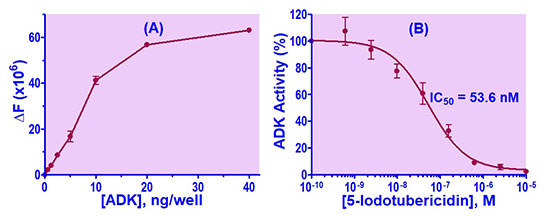
Publications
Rommel Mallaria, Elissa Swearingenb, Wei Liu, Arnold Ow, Stephen W. Young and Shu-Gui Huang* (2003) “A Generic High- throughput Screening Assay for Kinases: Protein Kinase A as an Example”. J. Biomol. Screen. 8: 198-204.
Catherine A. Hong, Elissa Swearingen, Rommel Mallari, Xiong Gao, Zhaodan Cao, Anne North, Stephen W. Young and Shu-Gui Huang* (2003) “Development of A High-Throughput Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Assay for TRAF6 Ubiquitin Polymerization”. Assay and Drug Development Technologies 1: 175-180.
Shu-Gui Huang* (2002) “Development of A High-throughput Screening Assay for Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Living Cells”. J. Biomol. Screen. 7: 383-389.
Ellyn Farrelly, M. Catherine Amaral, Lisa Marshall and Shu-Gui Huang* (2001) A high-throughput assay for mitochondrial membrane potential in permeabilized yeast cells. Analytical Biochemistry 293(2):269-276.
Tony Smith, John Chan, Donna Oksenberg, Roman Urfer, Dave Wexler, Arnie Ow, Liping Gao, Alanna McAlorum, and Shu-Gui Huang* (2004). A High-Throughput Turbidometric Assay for Screening Inhibitors of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Activity. J. Biomol. Screen. 9(7): 614-620.
David S. Wexler, Liping Gao, Francisco Anderson, Arnold Ow, Laszlo Nadasdi, Alanna McAlorum, Roman Urfer, and Shu-Gui Huang* (2005). “Linking Solubility and Permeability Assays for Maximum Throughput and Reproducibility”. J. Biomol. Screen. 10(4): 383-390.
Shu-Gui Huang (2005) “Progress from HTS to HTL: Current Strategies in Drug Lead Discovery” Review article in Trends in Pharmaceutical Research 1: 5-10.
David S. Wexler, Shu-Gui Huang, Roman Urfer (2004). “Replumbing the Pipeline: A small, biopharmaceutical company’s strategy for integrating lead optimization and ADMET screening”. Current Drug Discovery, May 2004: 35-38.
Shu-Gui Huang, Donna Oksenberg, Roman Urfer (2005). “High-throughput Turbidometric Assay for Screening Inhibitors of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Activity”. US 6,977,142.
Customer Testimonials




